Delete Orphaned Mailboxes in Exchange 2010
Admins of Exchange 2010 Purge Disconnected Mailboxes to bolster the security of their servers. Orphaned mailboxes or disconnected mailboxes occupies unnecessary space and slow down the Exchange Server. They occur when ever a mailbox fails to find its user connection agent inside an Active Directory.
It is equally likely that due to heavy mail traffic server itself disconnects the mailbox. SO to avoid this admins can set throttling policy in Exchange 2016. This can help to regulate user workload and may prevent disconnections that happen automatically.
The Microsoft Exchange mailboxes have an Active Directory of user account and the Exchange mailbox database. The mailbox configuration data is stored in Active Directory of user object. The mailbox database stores emails that is in the mailbox associated with the user account. When the mailbox object present in mailbox database is not associated an Active Directory of user account then it becomes disconnected or orphaned.
Exchange 2010 Purge Disconnected Mailboxes Know the Types
Disabled Mailboxes
There are two reasons behind disabling the mailboxes:
- When the mailboxes are deleted from Exchange Administration Center
- Disconnected by using PowerShell cmdlet Disable-Mailbox or Remove-Mailbox
However, Exchange holds back the deleted mailbox in database and then switches the mailbox to disable state. Whenever the admin disable a mailbox, the Exchange attributes are removed from Active Directory but user account is retained in Exchange Server. The retention of disabled mailboxes depends on the retention period, which is 30 days by default.
Soft Deleted Mailbox
Whenever the admin moves the mailbox from its database to a different mailbox database, Exchange does not completely delete the mailbox from the source database even when mailbox has been migrated to destination database. The mailbox in source database will retain the soft-deleted state. The retention of soft-deleted mailbox will depend on retention period imposed by the admin.
Disabling and Deleting a Mailbox in Exchange
Whenever the admin permanently deletes disconnected mailboxes, all the data in the mailbox is also removed from the Exchange mailbox database. Moreover, when admin permanently deletes any active mailbox, the Active Directory associated with user account is also deleted.
Therefore, the primary difference between deleting and disabling an Exchange mailbox is that when the admin disable the mailbox, its attributes are deleted from Active Directory but user’s mailbox can be retained.
Whereas in mailbox deletion one cannot get back their mailbox data from database as its Exchange attributes and Active Directory is deleted.
Note: There is an alternative method where admin can disconnect the mailbox instead of permanently deleting it. When the admin disconnects a mailbox object from Active Directory, by default, it remains in the mailbox database for 30 days. This gives Exchange admin the opportunity to reconnect or restore a mailbox data before it is purged from the database.
How to Delete Orphaned Mailboxes in Exchange 2010
Admin can use PowerShell commands to permanently disabled mailboxes from Exchange 2010.
There are some steps that user can take to delete the Orphaned or disabled mailboxes:
- User can clean all the tasks using
Command:clean-mailboxdatabase "user_mailbox_name"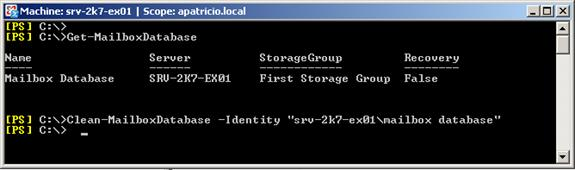
- Get the list of all disconnected Mailboxes present in database.
Command:Get-MailboxStatistics -Database “Database store name” | where {$_.DisconnectReason -eq “display name”}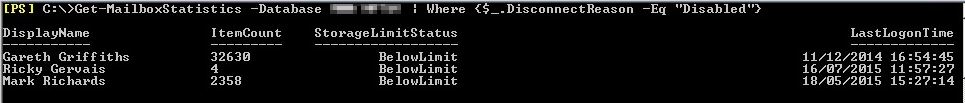
- After getting the list of disconnected mailboxes user can delete the mailbox from database using following commands:
- For permanently deleting the disabled mailbox:
Command:Remove-StoreMailbox -Database “Mailbox Database” -Identity"User_mailbox_name"-MailboxState Disabled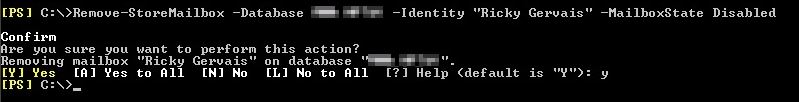
- For permanently deleting the soft deleted mailbox:
Command:Remove-StoreMailbox -Database “Mailbox database” -Identity "user_mailbox_name" -MailboxState SoftDelete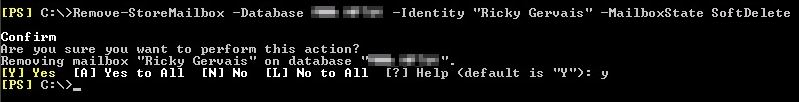
- For permanently deleting the disabled mailbox:
Conclusion
By using above mentioned procedure about How to Delete Orphaned Mailboxes in Exchange 2010, we can conclude that Exchange Server 2010 admin can easily delete the orphaned or disconnected mailboxes using PowerShell commands in an effective way. The above mentioned command can be executed either in PowerShell or in Exchange Management Shell (EMS) of Exchange Server 2010.
Frequently Asked Questions on How to Delete Orphaned Mailboxes in Exchange Server?
Why do orphan mailboxes still count as part of the Database size Quota?
Until permanent removal from the server, the disconnected, or even soft-deleted orphan mailboxes still occupy significant space in your server, thus counting towards the overall data volume.
Can I make my Exchange server send out a notice every time it detects a previously healthy mailbox in a now Orphan state?
Currently, no edition of the Exchange Server has this capability. However, you can add it on your own via PowerShell and Task Scheduler. It will allow you to automate disconnection detection in the Exchange server.
Is it safe for me to delete orphan mailboxes via PowerShell?
Depends on how much confidence you have in your abilities. Mistakes can happen to anyone. As safety is a matter of attitude, so double-check each parameter and mailbox name, and if possible, also retain a backup or the orphan in external storage outside of the scope of PowerShell commands.
How exactly does a disconnected mailbox affect the performance of an Exchange Server?
Despite being in a dormant state, the orphan mailboxes continue to possess a vast amount of information. This adds unnecessary load on the server, which slows and impacts other operations.
What happens when a user with an orphan mailbox tries to log in?
As the major cause of an orphan mailbox is the absence of the host account, it’s not possible for users with disconnected mailboxes to log in. In case login occurs, they will witness a blank mailbox with no data. Moreover, unless they possess Recipient Management or Organization Management roles, they can’t fix the issue and have to escalate it to the admin.